 Your Title Text
Your Title TextTypes of Gum Disease
Periodontal
(gum) diseases, including gingivitis and periodontitis, are serious
infections that, left untreated, can lead to tooth loss. The word
periodontal literally means "around the tooth." Periodontal disease is a
chronic bacterial infection that affects the gums and bone supporting
the teeth. Periodontal disease can affect one tooth or many teeth. It
begins when the bacteria in plaque (the sticky, colorless film that
constantly forms on your teeth) causes the gums to become inflamed.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the mildest form of periodontal disease. It causes the gums to become red, swollen, and bleed easily. There is usually little or no discomfort at this stage. Gingivitis is often caused by inadequate oral hygiene. Gingivitis is reversible with professional treatment and good oral home care.
Periodontitis
Untreated gingivitis can advance to periodontitis. With time, plaque can spread and grow below the gum line. Toxins produced by the bacteria in plaque irritate the gums. The toxins stimulate a chronic inflammatory response in which the body in essence turns on itself, and the tissues and bone that support the teeth are broken down and destroyed. Gums separate from the teeth, forming pockets (spaces between the teeth and gums) that become infected. As the disease progresses, the pockets deepen and more gum tissue and bone are destroyed. Often, this destructive process has very mild symptoms. Eventually, teeth can become loose and may have to be removed.
There are many forms of periodontitis. The most common ones include the following.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the mildest form of periodontal disease. It causes the gums to become red, swollen, and bleed easily. There is usually little or no discomfort at this stage. Gingivitis is often caused by inadequate oral hygiene. Gingivitis is reversible with professional treatment and good oral home care.
Periodontitis
Untreated gingivitis can advance to periodontitis. With time, plaque can spread and grow below the gum line. Toxins produced by the bacteria in plaque irritate the gums. The toxins stimulate a chronic inflammatory response in which the body in essence turns on itself, and the tissues and bone that support the teeth are broken down and destroyed. Gums separate from the teeth, forming pockets (spaces between the teeth and gums) that become infected. As the disease progresses, the pockets deepen and more gum tissue and bone are destroyed. Often, this destructive process has very mild symptoms. Eventually, teeth can become loose and may have to be removed.
There are many forms of periodontitis. The most common ones include the following.
Aggressive periodontitis occurs in patients who are otherwise clinically healthy. Common features include rapid attachment loss and bone destruction and familial aggregation. 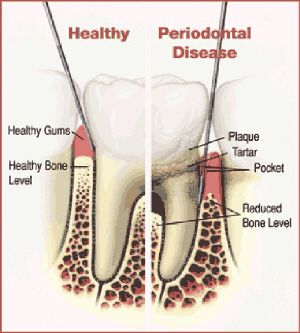
Chronic periodontitis results in inflammation within the supporting tissues of the teeth, progressive attachment and bone loss. This is the most frequently occurring form of periodontitis and is characterized by pocket formation and/or recession of the gingiva. It is prevalent in adults, but can occur at any age. Progression of attachment loss usually occurs slowly, but periods of rapid progression can occur. Periodontitis as a manifestation of systemic diseases often begins at a young age. Systemic conditions such as heart disease, respiratory disease, and diabetes are associated with this form of periodontitis.
Necrotizing periodontal disease is an infection characterized by necrosis of gingival tissues, periodontal ligament and alveolar bone. These lesions are most commonly observed in individuals with systemic conditions such as HIV infection, malnutrition and immunosuppression.

